Dracunculiasis, also known as guinea worm disease, remains a persistent parasitic infection caused by the Guinea worm parasite. This ancient illness has plagued humanity for centuries and continues to affect primarily impoverished communities in Africa. Transmission occurs when infected water is drunk, releasing the parasite larvae into the victim's system. Symptoms include painful blisters that develop on the body and ultimately lead to a long course of treatment.
Fortunately, recent efforts have made significant progress in controlling this disease. Medical professionals are working tirelessly to provide clean water, promote hygiene measures, and treat infected individuals.
- However, dracunculiasis remains a significant public health issue that requires continued attention and investment.
- The international community must remain committed to supporting disease control initiatives to ensure the complete elimination of this devastating illness.
The Signs and Recognition of Dracunculiasis
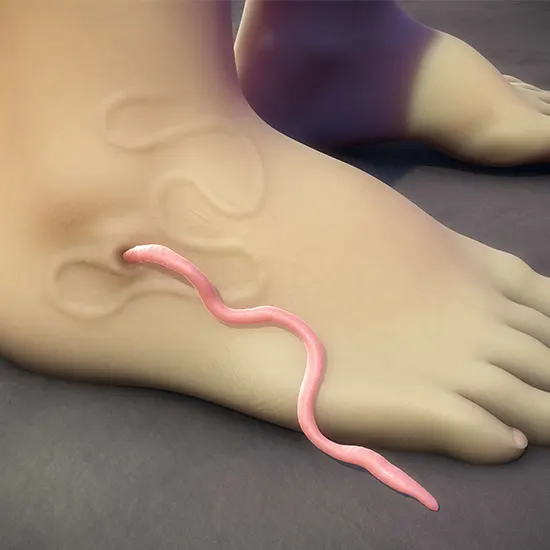
Dracunculiasis, also known as guinea worm disease, presents with characteristic clinical manifestations that are often uncomfortable. The most distinctive symptom is the protrusion of a serous blister on the skin, usually in areas of the body exposed to contact. This blister gradually enlarges and breaks open, releasing the mature adult guinea worm. The worm may extend from the lesion, causing intense burning pain and irritability. The patient often feels bouts of fever, nausea, and weakness as a result of the parasitic infection.
Diagnosing dracunculiasis relies primarily on observational examination of the characteristic lesion. The presence of a protruding worm is highly diagnostic. Biochemical testing may be employed to confirm the diagnosis, but it is not always necessary. It's important to note that early detection and treatment are crucial to prevent complications such as secondary infections and debilitating pain.
Dracunculiasis: Causes, Symptoms, and Transmission
Dracunculiasis, referred to as Guinea worm disease, is a debilitating parasitic infection caused by the nematode _Dracunculus medinensis_. It's transmitted through the consumption of infected water containing copepods – tiny crustaceans that harbor the microscopic larvae of the guinea worm. When an infected person drinks contaminated water, the larvae are released in their stomach and migrate to different tissues. After about a year, a painful blister develops on the skin, often near the legs or feet. To alleviate the pain, the affected person may immerse their limb in water, which causes the worm to emerge, continuing its life cycle by releasing larvae into the water.
The symptoms of Dracunculiasis are characterized by intense burning as the worm emerges from the skin. Other symptoms include fever, itching, and weakness. The infection can lead to secondary bacterial infections, joint damage, and even severe complications in some cases.
- Preventing Dracunculiasis involves
- Drinking treated water
- Boiling water before consumption
- Using protective footwear when walking in areas where infection is prevalent
- Educating communities about proper hygiene
Eradication Efforts for Dracunculiasis: Challenges and Successes
The control of dracunculiasis, also known as Guinea worm disease, has made remarkable strides in recent decades. While the incidence of cases has plummeted by over 99% since its peak in 1986, challenges remain in achieving complete elimination.
One major obstacle is the disease's reliance on access to contaminated water sources. Populations often lack safe water supply options, forcing them to rely on stagnant pools where Guinea worm larvae thrive. Additionally, outbreaks can reoccur in areas with weak public health infrastructure and limited surveillance capacity.
Despite these hurdles, significant successes have been recorded. International efforts have played a crucial role in providing funding, technical expertise, and community involvement. These initiatives focus on safe water provision, hygiene education, and the timely care of infected individuals.
The path towards complete eradication is ongoing and requires sustained dedication from both local and global stakeholders. Continued research into control strategies and innovative solutions are essential to ensure that dracunculiasis is ultimately consigned to the history books.
The Silent Killer: Addressing the Public Health Burden of Dracunculiasis
Dracunculiasis, commonly referred to guinea worm disease, remains a stubborn public health threat in certain regions of the world. This cruel parasitic infection impacts millions, causing intense pain and impairment. Transmission occurs through ingestion of contaminated water sources polluted with the Guinea worm larvae. Early detection and treatment are crucial to prevent the spread of this horrifying disease. While significant progress has been made in eradicating dracunculiasis, continued work are indispensable to obtain a world free from this silent killer.
Numerous interventions have been implemented to address dracunculiasis, including better water sanitation practices, community training, and effective treatment methods. It is a global responsibility to support these efforts and guarantee that everyone has access to safe water and proper healthcare. Jointly, we can overcome this long-standing disease and safeguard the health of future generations.
{Dracunculiasis Control Through Water Safety Initiatives|Dracunculiasis Elimination via Safe Drinking Water|Controlling Dracunculiasis with Improved Water Hygiene
Dracunculiasis, also known as Guinea worm disease, presents a serious parasitic infection spread through contaminated water sources. To combat this debilitating disease, it is crucial to focus on improving water safety and hygiene practices in affected communities.
- Implementing safe water storage techniques can significantly reduce the risk of transmission. Requires using protected wells, boiling or treating water before consumption, and storing it in clean containers.
- Maintaining cleanliness of water sources is essential to prevent the proliferation of Guinea worm larvae. This should be done community-led efforts to clear debris and ensure proper drainage.
- Informing communities about the transmission cycle of dracunculiasis and preventive measures is vital for behavioral change.
By investing in water safety initiatives, we can effectively control and ultimately eradicate this preventable disease, improving the health and well-being of vulnerable populations worldwide.
Global Collaboration in Eradicating Dracunculiasis
The eradication aim of dracunculiasis, also known as guinea-worm disease, represents a monumental endeavor for the global health community. This debilitating parasitic disease, transmitted through polluted water sources, has plagued communities in countries across Africa and Asia for centuries. To achieve its ultimate purpose, the international network has united behind a comprehensive eradication strategy. This joint effort involves diverse stakeholders, including governments, NGOs, researchers, and local communities. Through deployment of integrated programs that address water sanitation, disease surveillance, and patient care, progress has been made in decreasing the incidence of dracunculiasis. However, the fight is far from over. Sustained funding and unwavering commitment are crucial to ensuring the complete eradication of this persistent disease, leaving no one behind.
Innovative Solutions for Dracunculiasis Elimination
Dracunculiasis, also known as Guinea worm disease, is a debilitating parasitic illness that affects millions of people globally. Eradicating this disease requires a multi-pronged approach that focuses sustainable solutions. These strategies must be culturally appropriate and take into account the specific needs of affected communities. Key components include improving access to clean water through sustainable sanitation initiatives, promoting health education to raise awareness about transmission prevention, and providing effective care for infected individuals. Ultimately, successful eradication hinges on a collaborative effort involving governments, international organizations, local communities, and individuals who are dedicated to eliminating this scourge from our world.
Combating the Cycle: Preventing Dracunculiasis through Community Engagement
Dracunculiasis, also known as Guinea worm disease, poses a severe parasitic infection. It is spread through drinking contaminated water, and results in painful blisters on the legs, arms, or feet. For centuries, this disease has plagued communities in specific regions of Africa and Asia. However, with a concerted approach, we are making significant strides in its eradication.
One of the keystones of this fight is community engagement. Local communities play a vital role in preventing and controlling dracunculiasis.
Their insights of the environment, transmission patterns, and cultural practices plays a critical role.
Community-based interventions include:
- Promoting understanding
- Providing safe drinking water solutions
- Early detection and treatment
When communities are actively involved in all stages of the eradication process, it increases the effectiveness of our interventions. By working together, we can break the cycle.
Treatment Approaches for Dracunculiasis Cases
dracunculiasis eradicationDracunculiasis, also known as Guinea worm disease, presents a unique obstacle in clinical settings due to its prolonged incubation period and the need for careful management. Early detection is crucial, often relying on patient reports of painful ulcers appearing after weeks. Supportive care aims to alleviate pain and avoid secondary issues. Involving local communities in surveillance, sanitation initiatives, and safe water practices plays a vital role in eliminating the spread of this disease.
- Specific wound care with gentle sanitization and bandaging
- Raising of the affected limb to alleviate swelling
- Pain management using available medications as indicated
Monitoring and Scouting for Dracunculiasis Resurgence
Dracunculiasis, also known as Guinea worm disease, is a debilitating parasitic infection that was once widespread. While significant progress has been made in its eradication, the potential for resurgence remains a concern. Continuous monitoring and proactive surveillance are crucial to detecting any new outbreaks and preventing their spread. This involves deploying robust systems for reporting suspected cases, conducting epidemiological investigations, and tracking the movement of infected individuals.
A meticulous surveillance network requires the partnership of various stakeholders, including health officials, local communities, and international organizations. By sharing information and resources, these entities can work together to effectively monitor the disease burden and address any potential threats.
Early detection of dracunculiasis cases is essential for containing outbreaks and preventing further transmission. This requires improving public awareness about the disease, its symptoms, and preventative measures. Educating communities about the importance of safe water practices and providing access to clean drinking water sources are key strategies in mitigating the risk of resurgence.
Regular assessments of surveillance programs are essential to ensure their effectiveness. By examining data, identifying trends, and adapting strategies, we can strengthen our capacity to combat dracunculiasis and ultimately achieve its eradication.